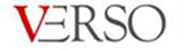Agricultural biogas
Farms produce large amounts of waste. Anaerobic digestion is one of the best, ecologically acceptable forms of its utilisation. Methane fermentation of agricultural waste, especially the waste from animal production and agro-food processing, allows to obtain energy in the form of biogas, reduce ecological threat to the natural environment and manufacture an organic fertilizer that is free from contaminants and odour. Anaerobic digestion of livestock excrement in the context of using it as a fertilizer gives the following benefits:
- reduction of the amount of nitrate nitrogen and the resulting increase of the amount of ammonia nitrogen,
- ability to maintain humus balance in the soil,
- weed seed destruction,
- elimination of pathogens,
- reduced use of chemical fertilizers,
- reduced risk of underground and surface water pollution,
- reduced proliferation of pathogens present in animal excrement.
The current data on the number of agricultural biogas plants in Poland can be found on the website of the National Center for Agricultural Support (KOWR) which keeps and publishes a register of agricultural biogas manufacturers.
The diagram below presents what substrates were used by agricultural biogas plants in 2015.